
购物车0
产品总数:61419

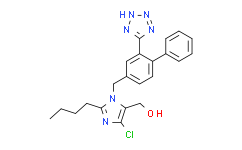
| 商品编号 | 规格 | 价格 | 会员价 | 是否有货 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL14770-500mg | 500mg | ¥328.00 | 请登录 |
|
|
| PL14770-1g | 1g | ¥413.00 | 请登录 |
|
|
| PL14770-5g | 5g | ¥965.00 | 请登录 |
|
|
| PL14770-10g | 10g | 询价 | 询价 |
|
|
| PL14770-50g | 50g | 询价 | 询价 |
|
|
| PL14770-10mM*1mLinDMSO | 10mM*1mLinDMSO | ¥803.00 | 请登录 |
|
|
| PL14770-1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | ¥413.00 | 请登录 |
|
 扫码关注公众号
扫码关注公众号